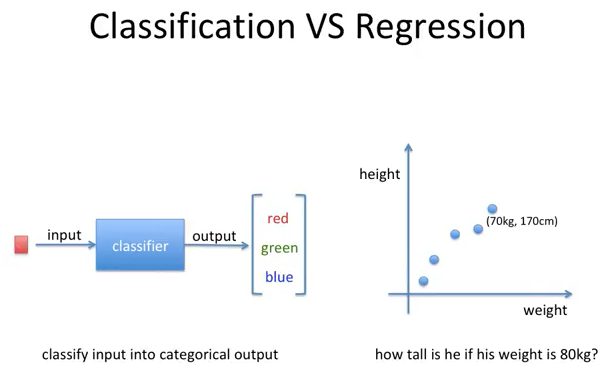
eg: House Price Prediction, Stock Price Prediction, Height-Weight Prediction.
eg: House Price Prediction, Stock Price Prediction, Height-Weight Prediction.
The majority of practical machine learning uses supervised learning.
Supervised learning is where you have input variables (x) and an output variable (Y) and you use an algorithm
to learn the mapping function from the input to the output.
Y = f(X)
The goal is to approximate the mapping function so well that when you have new input data (x) that you can predict the output variables (Y)
for that data.
It is called supervised learning because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of
as a teacher supervising the learning process.
We know the correct answers, the algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training
data and is corrected by the teacher.
Learning stops when the algorithm achieves an acceptable level of performance.
Supervised learning problems can be further grouped into regression and classification problems.
